Flutter Common Packages
- (0 Reviews)
- 13 students enrolled
Flutter Common Packages
When building Flutter apps, developers often rely on various packages to simplify tasks, enhance functionality, and speed up development.
- (0 Reviews)
- 13 students enrolled
Requirements
- When building Flutter apps, developers often rely on various packages to simplify tasks, enhance functionality, and speed up development.
Description
Detailed Description of Common Flutter Packages 1. get (GetX) Purpose: Lightweight and powerful solution for state management, routing/navigation, and dependency injection. Usage: Simplifies management of app state with reactive programming, easy navigation without context, and automatic dependency handling. Why Use: Minimal boilerplate, fast, and efficient for medium to large apps. 2. dio Purpose: Advanced HTTP client for Flutter. Usage: Used to perform network requests (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) with features like interceptors, global configuration, request cancellation, file uploads/downloads, and error handling. Why Use: More flexible and feature-rich compared to the basic http package. 3. shared_preferences Purpose: Simple key-value persistent storage on the device. Usage: Store small pieces of data like user settings, login tokens, flags, and preferences locally. Why Use: Easy to use and persists data even when the app restarts. 4. permissions Purpose: Manage app permissions on Android and iOS (e.g., camera, storage, location). Usage: Request, check, and handle user permissions at runtime to ensure app access to device features. Why Use: Simplifies permission handling with a unified API. 5. path_provider Purpose: Provides platform-specific filesystem paths. Usage: Access directories such as temporary folder, application documents directory, or external storage to save files. Why Use: Abstracts the platform differences for file storage locations. 6. sqflite Purpose: SQLite plugin for Flutter for local database management. Usage: Create, query, update, and manage relational data stored in a local SQLite database. Why Use: Essential for apps requiring structured offline data storage and complex querying. 7. connectivity_plus Purpose: Check network connectivity status (WiFi, mobile, offline). Usage: Monitor real-time internet connection changes and adapt app behavior accordingly (e.g., offline mode). Why Use: Ensures app handles network issues gracefully. 8. url_launcher Purpose: Launch URLs or external apps. Usage: Open websites, phone dialer, SMS, email client, or map apps directly from your Flutter app. Why Use: Easily integrates external links and communication actions. 9. share_plus Purpose: Share content (text, files, links) with other apps. Usage: Allow users to share app content through social media, messaging apps, email, etc. Why Use: Enables native share dialogs across platforms with minimal effort. 10. logging Purpose: Flexible logging framework. Usage: Manage and record log messages at different levels (info, warning, error), helpful during development and debugging. Why Use: Keeps logs organized and supports custom output formats. 11. image_picker Purpose: Pick images and videos from gallery or camera. Usage: Allow users to select or capture media for profile pictures, posts, uploads, etc. Why Use: Provides seamless integration with device camera and gallery. 12. cached_network_image Purpose: Load and cache network images efficiently. Usage: Downloads images from the internet and caches them locally to improve performance and reduce data usage. ••Why Use: Optimizes image loading and user experience in image-heavy apps.
Recent Courses
- January, 29th 2026
- 7
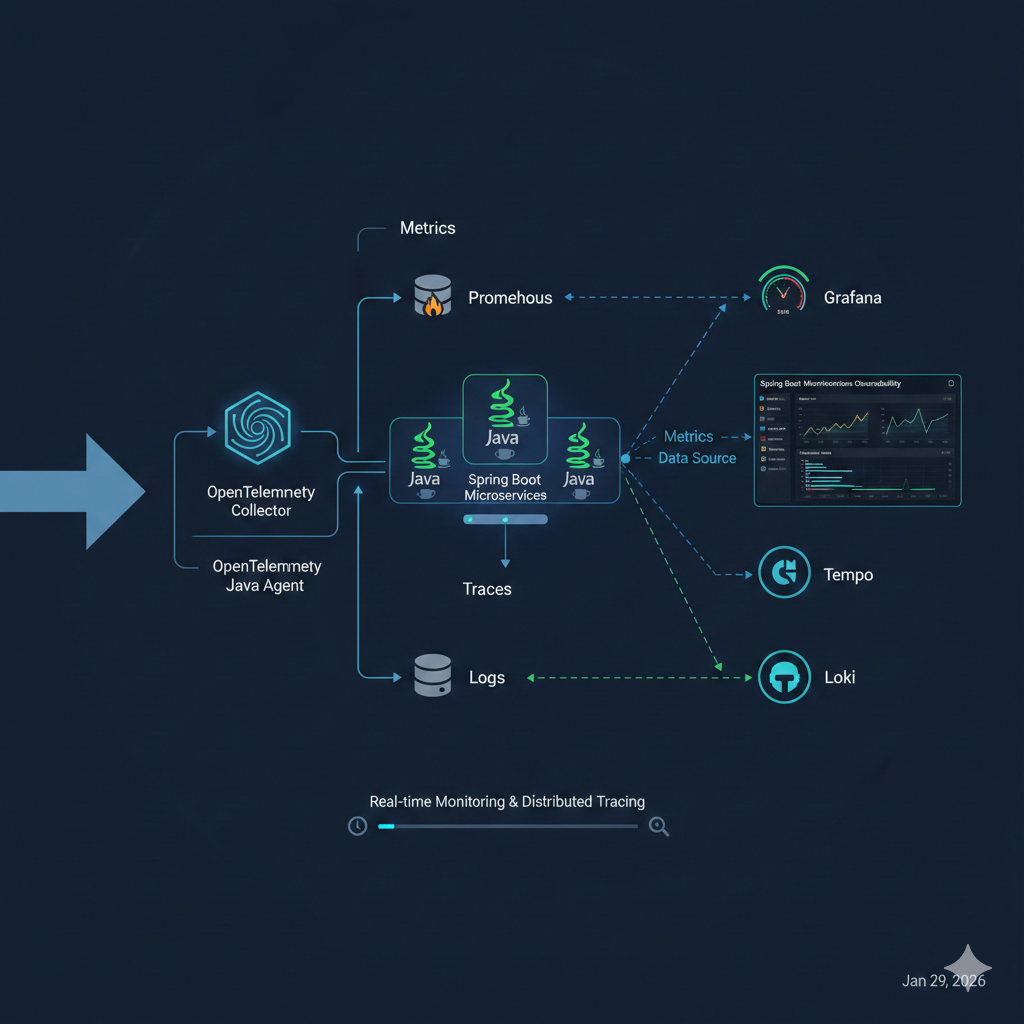
This training introduces Prometheus and Grafana, two core tools for modern monitoring and observability.
- Free
- January, 19th 2026
- 13
An introductory guide to Vue.js covering its core concepts, features, and how to get started building modern web applications..
- Free
- January, 14th 2026
- 13
Flutter – API Integration with JSON Parsing and UI
- Free
About Instructor

 Categories
Categories